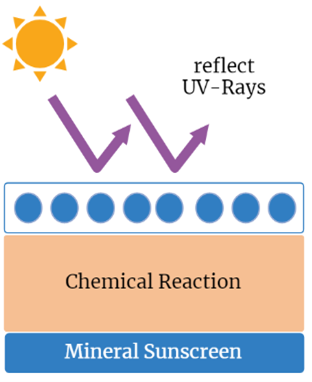
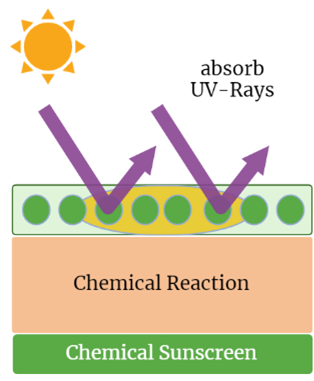
The Difference Between Mineral and Chemical Sunscreens: Which is Better?
Introduction:
A common product that helps shield the skin from the sun’s damaging rays is sunscreen. It functions by absorbing or reflecting ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, which can harm the skin and raise the risk of developing skin cancer. Active ingredients found in most sunscreens include zinc oxide and titanium dioxide. which are good at blocking UVA and UVB rays. The sun protection factor (SPF), which represents the degree of protection offered against UVB rays, is used to gauge how effective a sunscreen is. A higher SPF rating means that you will be better protected from sunburn.
To ensure the best protection, sunscreen must be applied correctly. Apply sunscreen 15 to 30 minutes prior to going outside, reapplying every two hours, or immediately after swimming or perspiring. Additionally, it’s crucial to apply sunscreen liberally and frequently, especially if you plan to spend a lot of time outdoors. The variety of sunscreen products on the market, including creams, lotions, sprays, and sticks, makes it simple to select one that is suitable for your skin type and way of life.
While using sunscreen to protect the skin from the sun is an effective strategy, it shouldn’t be the only one. It’s also important to seek shade during the hottest part of the day and to wear protective clothing, such as hats and long-sleeved shirts. It’s crucial to schedule routine dermatologist visits for skin exams and to be aware of the symptoms of skin cancer. By being proactive about sun protection, you can lessen your risk of skin cancer and other health problems while still taking advantage of the great outdoors.
However, it should be noted that all sunscreens are not identical. There are two primary categories of sunscreen, chemical, and mineral, and each type has its advantages and disadvantages.
Chemical and Mineral Sunscreen:
Both chemical and mineral sunscreen have not been classified as unsafe by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which is in charge of regulating sunscreen products. To update the legal requirements for sunscreen products sold in the US, the FDA however proposed a rule in February 2019. The FDA requested additional safety data for 12 active ingredients that are typically found in chemical sunscreens as part of this rule (FDA 2019).
Four sunscreen chemicals are absorbed into the bloodstream at levels above what the FDA requires for topical medications to go through safety studies, according to a clinical trial that was published in May 2019 in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA). A related study that examined six sunscreen chemicals and was released in January 2020 came to similar conclusions (Matta, Zusterzeel et al. 2019).
Despite these results, sunscreen is not recommended by the studies’ authors because sun exposure carries much greater known health risks. However, due to worries that they may disrupt hormones and trigger allergic reactions, the Environmental Working Group (EWG) advises against chemical sunscreens that contain oxybenzone. Furthermore, a review that appeared in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in January 2019 discovered that common chemical sunscreen ingredients like oxybenzone may harm coral reefs (EWG 2019).
Comparison between Chemical Sunscreen and Mineral Sunscreen
On the other hand, the FDA generally recognises mineral sunscreens containing zinc oxide and titanium oxide as safe and effective. According to a study published in the journal Nature Scientific Reports in May 2021, methylene blue might be a good replacement ingredient for zinc oxide in sunscreen because it effectively blocks UVA and UVB rays while being environmentally safe.
The Pros and Cons of Chemical Sunscreen:
Chemical sunscreens are a popular choice among people due to their ease of application and lack of white residue on the skin, which is a common issue with mineral sunscreens. In addition, chemical sunscreens are known to perform better on consumer tests in terms of providing protection against UV rays. However, it’s important to note that chemical sunscreens can cause adverse skin reactions in some individuals, especially those with sensitive skin (SCHILDHOUSE 2022).
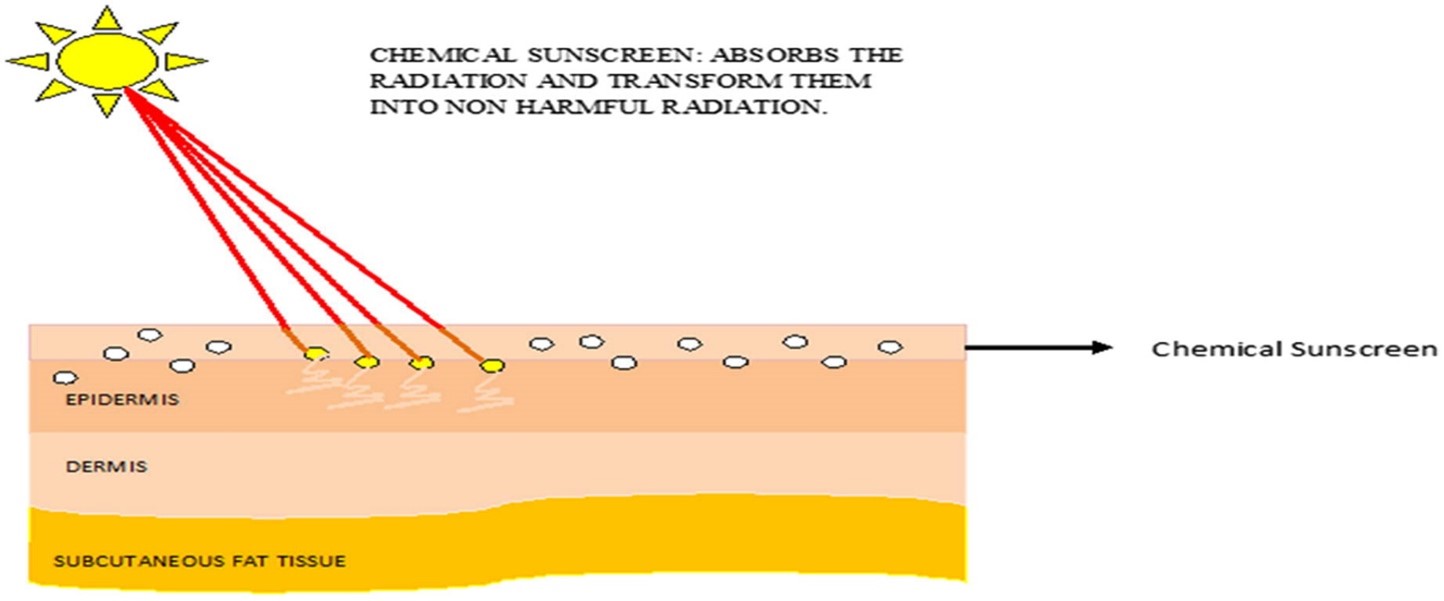
Graphical representation of the mechanism of action of chemical sunscreen (Jain, Rahi et al. 2017)
According to Dr. Ploch, allergic reactions are a possible side effect of using chemical sunscreens, which can lead to symptoms such as rashes, itching, and hives. Furthermore, people with certain skin conditions like melasma and rosacea may experience worsening of their symptoms when using chemical sunscreens. Melasma is a skin condition that causes brown patches on the face, forearms, and neck, while rosacea causes red patches and small pimples on the cheeks, nose, and forehead. These conditions can be exacerbated by the chemicals present in chemical sunscreens, making them an unsuitable option for some individuals (Bedosky 2021).
Overall, while chemical sunscreens may be an effective choice for many people, those with sensitive skin or certain skin conditions should consult with a dermatologist to determine the best sunscreen option for their needs.
The Pros and Cons of Mineral Sunscreen:
Dermatologists advise people who are worried about long-term exposure to chemical ingredients to use mineral sunscreens because they are a safer alternative. The FDA generally recognises titanium dioxide and zinc oxide, the two most prevalent ingredients in mineral sunscreens, as being both safe and effective. Mineral sunscreens are a practical choice because they provide protection right away without having to wait for them to be absorbed into the skin. Children, those with melisma, and those with sensitive skin can all use them (Bedosky 2021).
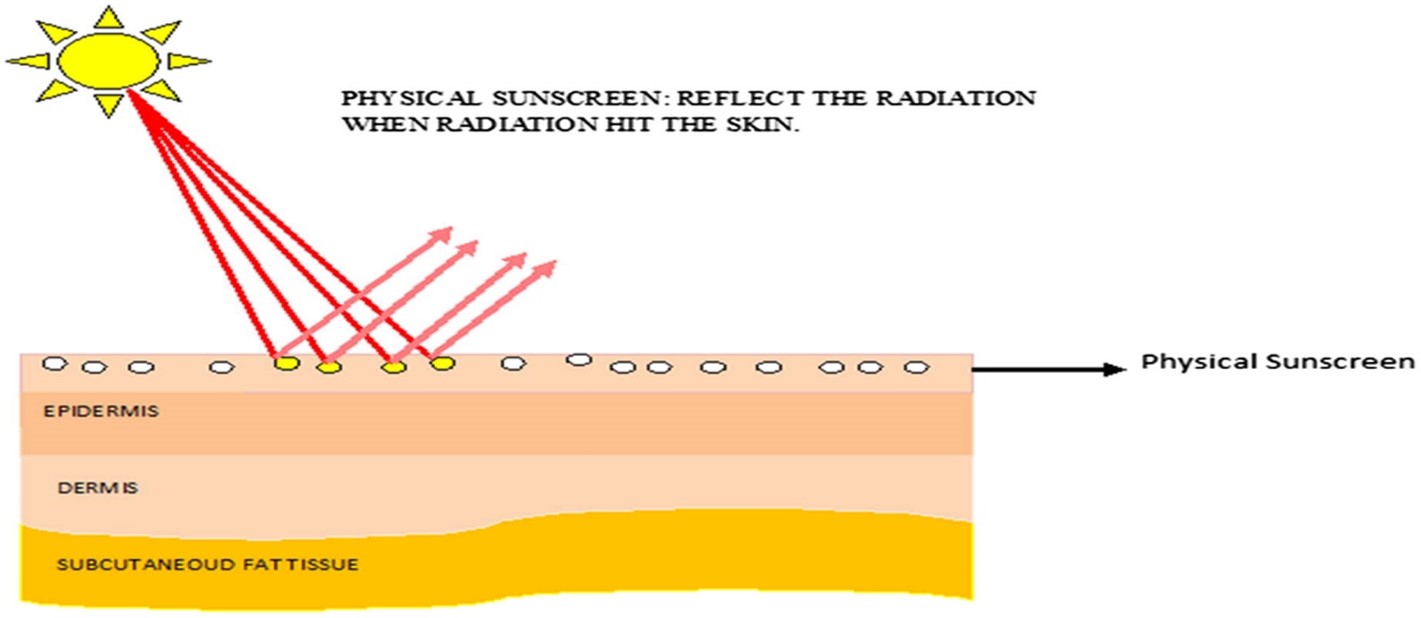
Graphical representation of the mechanism of action of chemical sunscreen (Jain, Rahi et al. 2017)
However, mineral sunscreens may cause breakouts in individuals who are prone to acne since they are thick and sit on top of the skin. A combination of mineral and chemical sunscreen ingredients may be beneficial for people with acne-prone or combination skin. Mineral sunscreens are harder to apply and tend to leave a white film on the skin, but there are options available that do not leave a white cast. Dermatologist-recommended brands include EltaMD, Alastin, and Isdin (SCHILDHOUSE 2022).
Which is Better?
According to Dr. Ploch, mineral sunscreens are a healthier option compared to chemical sunscreens, which she compares to fast food. Although mineral sunscreens take longer to apply and require more frequent reapplication, they are likely safer for long-term use. However, even if mineral sunscreen is not an option, it is better to use any type of sunscreen than not to use any at all. The FDA recommends using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher and reapplying at least every two hours to protect against both UVA and UVB rays.